局面 ( x , y ) x , y > 0 (x,y)~~~ x,y>0 ( x , y ) x , y > 0
操作 ( x , y ) → ( a , b ) a + b = x (x,y)\rightarrow(a,b)~~~a+b=x ( x , y ) → ( a , b ) a + b = x a + b = y a+b=y a + b = y
x , y ≤ 2 × 1 0 9 x,y\le 2\times 10^9 x , y ≤ 2 × 1 0 9
先手必败还是必胜?
首先打个表,朴素算 sg \operatorname{sg} s g
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 std::map<pii, int > sg; int calc (pii c) if (sg.count (c)) return sg[c]; std::vector<int > s; rep (i, 1 , c.first - 1 ) s.push_back (calc ({i, c.first - i})); rep (i, 1 , c.second - 1 ) s.push_back (calc ({i, c.second - i})); std::sort (s.begin (), s.end ()); s.erase (std::unique (s.begin (), s.end ()), s.end ()); int lst = -1 ; for (auto i : s) { if (i != lst + 1 ) return sg[c] = lst + 1 ; lst = i; } return sg[c] = lst + 1 ; }
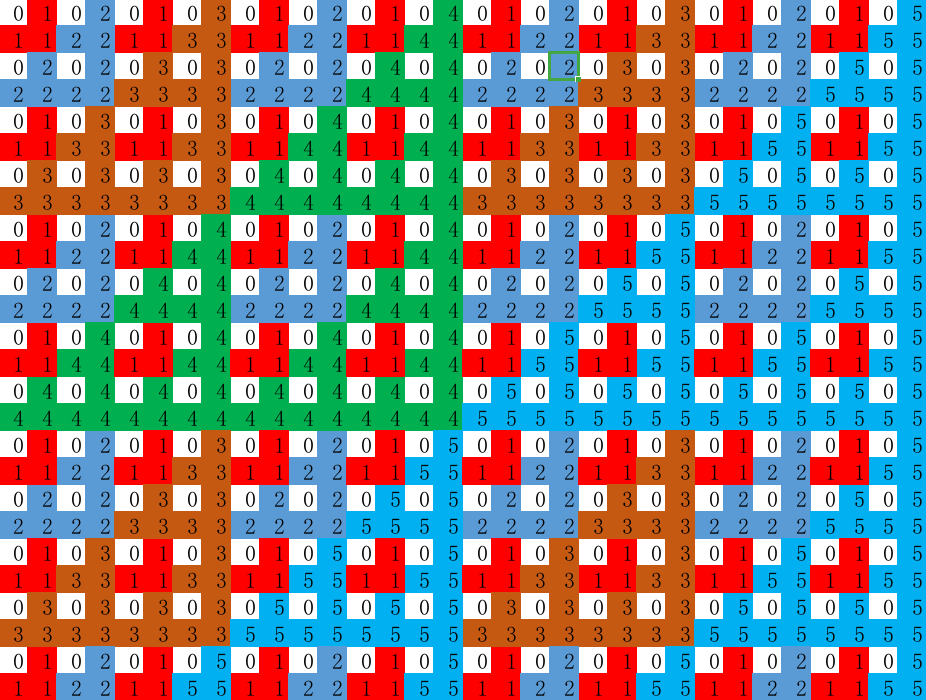
然后输到 Excel
非常的有规律
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 #define c(x, p) (x % p ? x % p : p) int sg (ui x, ui y) for (ui i = 0 , p = 2 ; i < 31 ; i++, p *= 2 ) { if ((c (x, p) <= p / 2 ) && (c (y, p) <= p / 2 )) return i; } return 31 ; }
i i i if 中的条件意思是在正方形的左上角 1 / 4 1/4 1 / 4
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 #include <algorithm> #include <cassert> #include <cmath> #include <cstdio> #include <cstring> #include <deque> #include <iostream> #include <map> #include <queue> #include <set> #include <stack> #include <string> #include <utility> #include <vector> #define rep(i, l, r) for (int i = (l); i <= (r); ++i) #define per(i, l, r) for (int i = (l); i >= (r); --i) using std::cerr;using std::cin;using std::cout;using std::endl;using std::make_pair;using std::pair;typedef pair<int , int > pii;typedef long long ll;typedef unsigned int ui;typedef unsigned long long ull;#define c(x, p) (x % p ? x % p : p) int sg (ui x, ui y) for (ui i = 0 , p = 2 ; i < 31 ; i++, p *= 2 ) { if ((c (x, p) <= p / 2 ) && (c (y, p) <= p / 2 )) return i; } return 31 ; } int main () #ifdef LOCAL freopen ("input" , "r" , stdin); #endif std::ios::sync_with_stdio (false ); cout.tie (0 ); int T; cin >> T; while (T--) { cerr << "doing " << T << endl; int n; cin >> n; n /= 2 ; int ans = 0 ; rep (i, 1 , n) { int x, y; cin >> x >> y; ans ^= sg (x, y); } cout << (ans ? "YES" : "NO" ) << std::endl; } return 0 ; }